If you are responsible for managing customer service operations, you are likely familiar with IVR (Interactive Voice Response) systems. These automated systems have been a staple of call centers for decades, helping route calls and handle simple queries without the need for human intervention.
But as technology evolves, Voice AI is becoming a game-changer in the customer experience space. While both IVR and Voice AI involve interacting with customers over the phone or voice channels, they are fundamentally different in how they operate and the kind of experience they deliver.
In this article, we will break down the key differences between IVR and Voice AI, explore when each tool makes the most sense, and discuss how they can actually work together to strengthen your service operations.
What Is IVR?
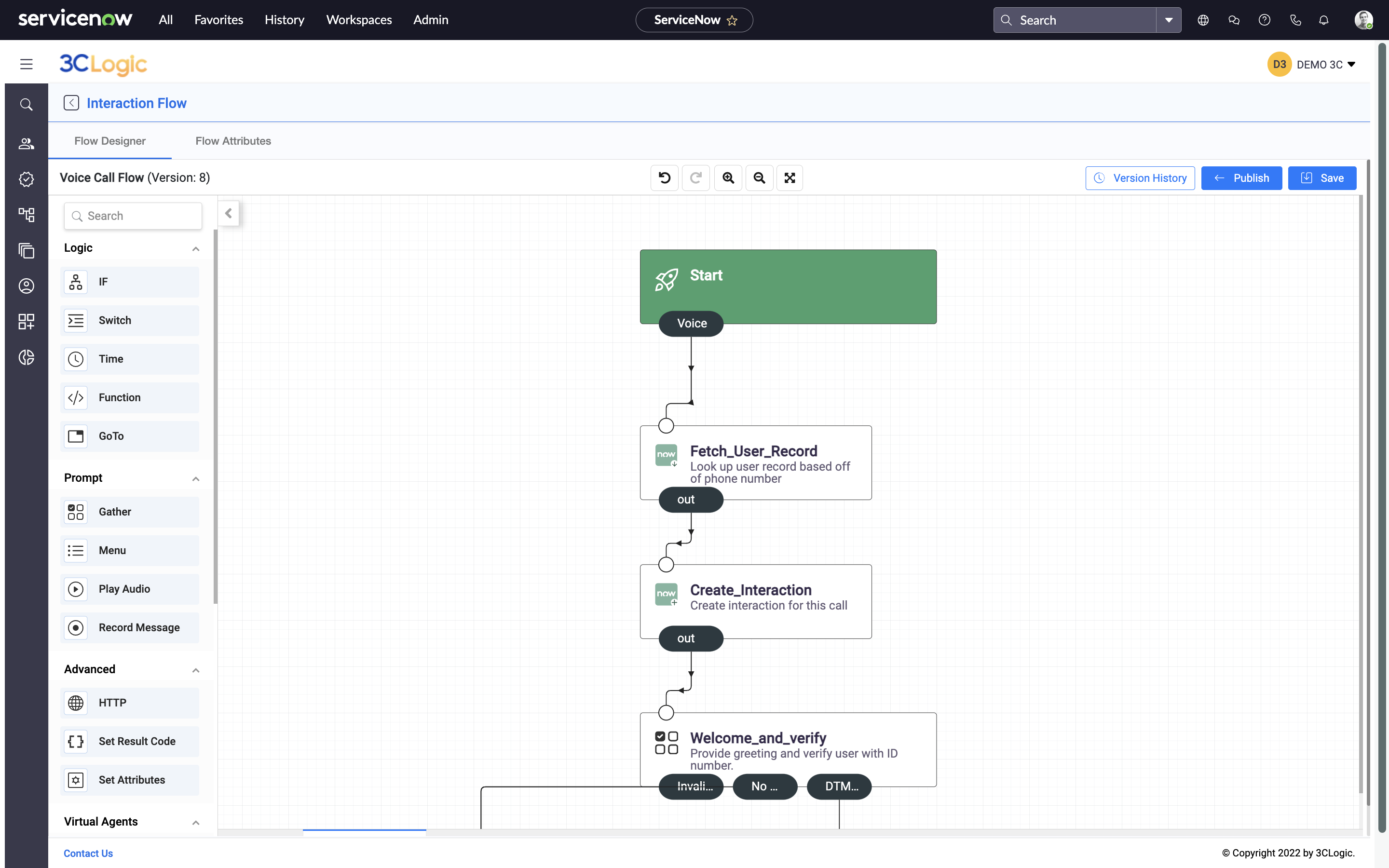
3CLogic's IVR solution for ServiceNow
An IVR (Interactive Voice Response) system is an automated phone solution that lets callers navigate menus using keypad inputs or limited speech recognition. It’s best known for the familiar “press 1 for support, press 2 for billing” experience.
IVRs are deterministic by design, meaning they follow fixed, rule-based workflows. Every path is predefined, so caller inputs lead to predictable, consistent outcomes. This makes IVRs reliable and scalable, especially in high-volume environments. While often associated with simple tasks like routing or balance inquiries, IVRs can handle more complex scenarios, particularly when integrated with CRM systems. This allows for some personalization, such as greeting a caller by name or surfacing account-specific options.
However, IVRs can only address what they’ve been explicitly programmed to handle. Each scenario must be mapped out in advance. If a request falls outside of those flows, the system typically escalates to a live agent.
In short, IVRs are a powerful tool for delivering structured and scalable service experiences. They are ideal for environments where customer needs are well-understood, predictable, and can be effectively addressed through a menu-driven approach.
What Is Voice AI?
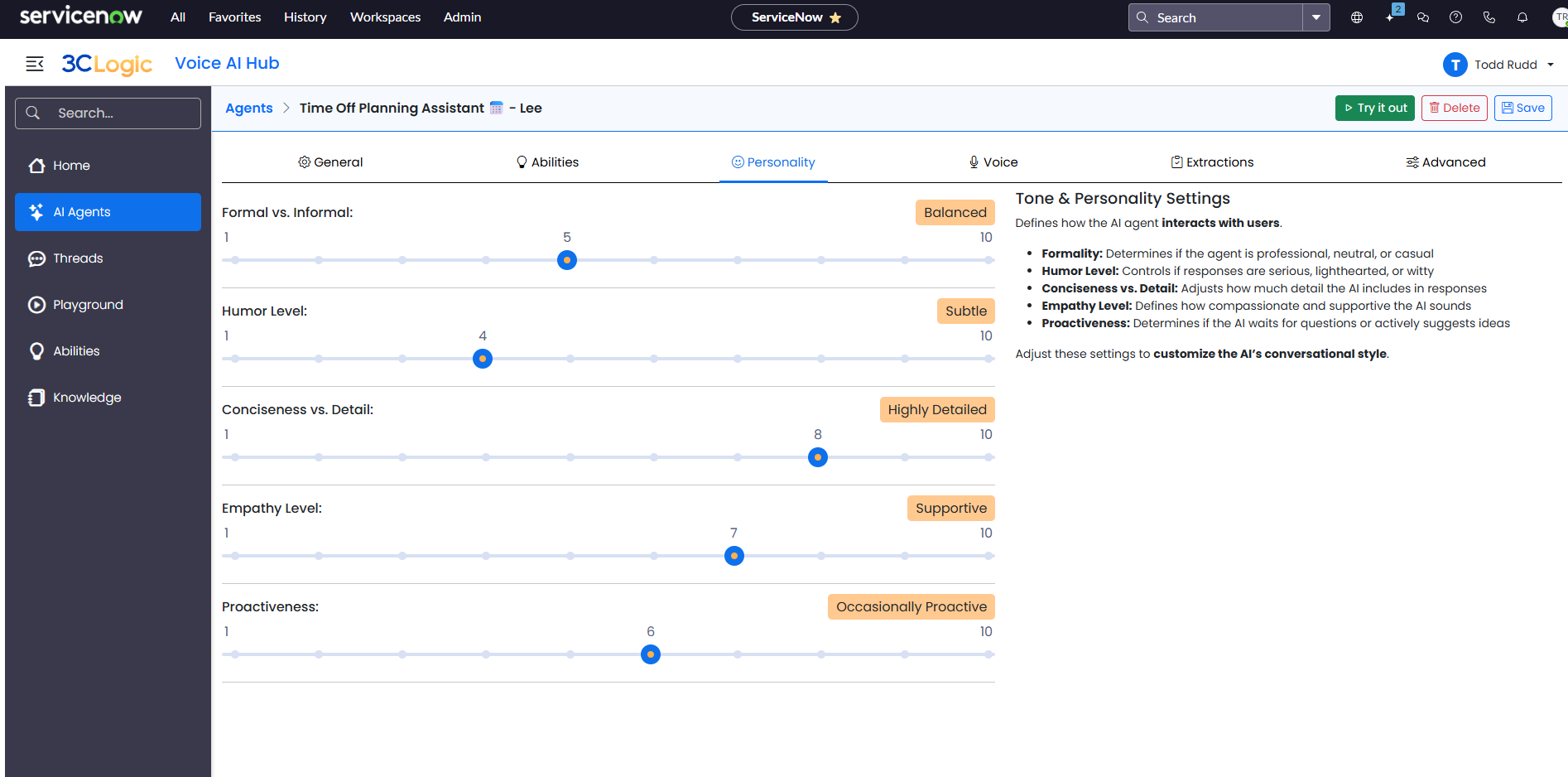
3CLogic's Voice AI Hub
Voice AI refers to conversational systems powered by artificial intelligence and natural language processing that allow users to interact through spoken language in a more natural, free-flowing way. Unlike IVRs, which follow fixed menus, Voice AI understands and responds to open-ended questions and phrases like “I need help with my internet” or “What’s my account balance?”
Voice AI is probabilistic in nature. Instead of relying on rigid, predefined workflows, it interprets intent based on language patterns, context, and data. Its logic is shaped by prompt engineering, where behavior is guided through designed inputs and conversational cues rather than static menu structures. This enables the system to handle a wide range of scenarios, including those it has not been explicitly programmed for. It considers multiple possible interpretations and selects the most likely response, allowing for more dynamic and flexible interactions.
Because of this, Voice AI is well-suited for managing complex, multi-turn conversations where users might ask follow-up questions, shift topics, or require personalized support. It can integrate deeply with backend systems to perform tasks such as scheduling appointments, resetting passwords, or checking order status, all within the flow of natural conversation.
While Voice AI requires more sophisticated infrastructure and training than traditional IVR, it delivers a more human-like experience that adapts in real time. It excels in environments where customer intent is varied and responsiveness matters.
Comparison Chart
| Feature | IVR (Interactive Voice Response) | Voice AI |
|---|---|---|
|
Core Logic |
Deterministic — follows fixed, rule-based workflows |
Probabilistic — interprets intent using AI and natural language |
|
Interaction Style |
Menu-driven (keypad or basic voice commands) |
Conversational, open-ended speech |
|
Flexibility |
Rigid — limited to predefined options |
Adaptive — can handle varied and evolving user inputs |
|
Complexity Handling |
Capable, but must be fully scripted |
Handles simple to complex scenarios dynamically |
|
Personalization |
Possible with CRM integration, but must be built into flows |
Deep personalization in real time through contextual understanding (i.e.: CRM, Knowledge Article, etc.) |
|
Queuing and Routing |
Built-in queueing and routing capabilities |
Requires integration with IVR or telephony for routing and hold |
|
System Integration |
Integrates with CRMs and databases within structured flows |
Integrates with systems dynamically based on user intent |
|
Error Handling |
Defaults to fallback menus or agent transfer when off-script |
Can clarify, recover, or re-route based on understanding gaps |
|
Maintenance |
Easier to maintain but time-consuming to expand |
Requires training and monitoring but scales more fluidly |
|
Security and Compliance |
Easier to secure due to structured flows |
Requires stricter controls and AI governance for sensitive unstructured data |
|
User Experience |
Predictable and consistent |
Natural, intuitive, and responsive |
|
Best For |
High-volume, routine, and clearly defined interactions |
Complex, varied, or high-value customer conversations |
How IVR and Voice AI Can Work Together
IVR and Voice AI are not competing technologies. They are complementary parts of a well-rounded voice strategy, each bringing unique strengths to the customer experience. When used together, they can improve service delivery, reduce operational strain, and create a more seamless and satisfying interaction for callers.
In one common approach, Voice AI serves as the first point of contact. It greets the caller, understands natural language input, and attempts to resolve the inquiry through conversation. If the request is beyond the Voice AI's scope, lacks sufficient data, or requires escalation, control can then shift to an IVR system. The IVR, with its strong call routing and queueing capabilities, handles the operational tasks that Voice AI is not designed to manage. In this setup, Voice AI provides the intelligence while IVR provides the structure needed to manage volume and escalation.
Alternatively, some organizations place IVR at the front of the call flow. The IVR quickly collects basic inputs, such as account numbers or language preferences, and routes calls based on initial categories. If a caller’s needs fall into a more complex or open-ended category, the system can seamlessly hand off the interaction to Voice AI. The AI then engages in deeper conversation, understanding context and helping resolve the issue in a more personalized and conversational way.
There are also hybrid models where IVR and Voice AI share responsibilities throughout a single interaction. For example, the IVR might handle authentication at the beginning of the call, after which Voice AI takes over to address the user’s request. If the resolution requires queueing or scheduling, the IVR might resume control to manage those final steps. When properly integrated, both systems can pass along relevant context such as the caller’s information, previous actions, or inferred intent. This eliminates redundancy and helps maintain continuity throughout the interaction.
Ultimately, combining IVR and Voice AI allows organizations to deliver service that is both efficient and responsive. IVR ensures structure and reliability, while Voice AI provides adaptability and conversational fluency. Together, they form a more intelligent, flexible, and scalable voice solution.
Final Thoughts
For service desk managers and customer support leaders, the decision between IVR and Voice AI should not be framed as either-or. Instead, consider them as complementary technologies that can be used strategically depending on the nature of your call volume, customer expectations, and available resources.
Ultimately, combining IVR and Voice AI allows organizations to deliver service that is both efficient and responsive. IVR ensures structure and reliability, while Voice AI provides adaptability and conversational fluency. Together, they form a more intelligent, flexible, and scalable voice solution.



